hackthevote
Flip State
Challenge Description:
We want you to devise a new secure method of encrypting votes which does not rely on any sort of key (that way the baddies can’t steal the key!). Also the bureaucrats have been reading some crypto blogs and want you to do it with only a single bit flip on some random data. They assure us that you can do it as you are an expert after all :) To get the flag you must successfully encrypt and decrypt 20000 votes in a row. Note: You are not supposed to escape the sandbox, you are supposed to pass the checks. Good luck :)
server: flipstate.hackthe.vote:43690:
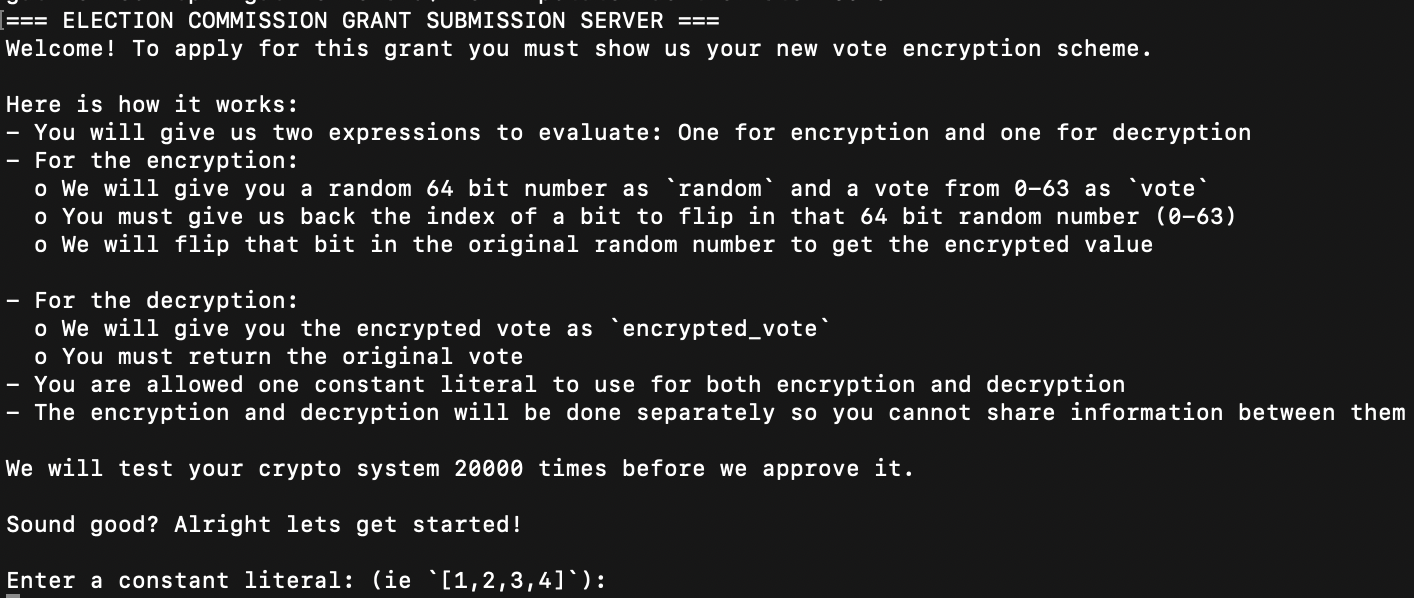
So, this challenge asks me to create an encryption algorithm with a corresponding decryption algorithm. The encryption should only flip a single bit, and I’m assuming that the constant literal asked for by the server indicates the index of which bit will be flipped. The decryption algorithm needs to look like the reverse of the encryption algorithm, but I’m a little lost on how to account for the shifted bit. Like I said earlier, I think that the constant literal asked for is the index of the flipped bit, so if the encryption looks like (‘vote+100’), the decryption would need to look like (‘encrypted_vote+100’), with the added exception of accounting for the flipped bit. So, I think that decryption would need to look like, ‘encrypted_vote ^ (1 « constant_literal)-100’. However, when I run the program with these inputs, I continue to receive the error: “Sorry your system did not stand up to testing. Please feel free to reapply in the future!”. Not entirely sure why this wouldn’t work.
Registration Database
Challenge Description:
We’ve found some voter registration data stored in a database with public access. Unfortunately, they’re using AES encryption with secure key generation.
handout:
import secrets
import socketserver
import string
from cryptography.hazmat.backends import default_backend
from cryptography.hazmat.primitives import hashes
from cryptography.hazmat.primitives.ciphers.aead import AESGCM
from cryptography.hazmat.primitives.kdf.pbkdf2 import PBKDF2HMAC
PLAINTEXTS = [
b"Sandra R. Jackson;reg2;1728 Goldie Lane",
b"Leo N. Shatley;reg1;2251 Sunburst Drive",
b"Faye S. Ramsey;reg2;3186 Froebre Street",
b"Charles C. Felix;reg3;2726 Locust Court",
]
with open("flag.txt", "rb") as f:
PLAINTEXTS.append(f.read().strip())
def challenge(ioin, ioout):
ioout.write(b"hello\n")
key = secrets.token_bytes(nbytes=None)
salt = secrets.token_bytes(nbytes=16)
aesgcm = AESGCM(key)
attempted_nonces = list()
for attempt in range(len(PLAINTEXTS)):
nonce = ioin.readline().strip()
if (
len(nonce) < 10
or len(nonce) > 100
or nonce in attempted_nonces
or not all([c in string.printable.encode() for c in nonce])
):
ioout.write(b"no\n")
return
attempted_nonces.append(nonce)
ioout.write(
aesgcm.encrypt(
PBKDF2HMAC(
algorithm=hashes.MD5(),
length=32,
salt=salt,
iterations=100000,
backend=default_backend(),
).derive(nonce),
secrets.choice(PLAINTEXTS),
None,
)
.hex()
.encode()
+ b"\n"
)
class MyTCPHandler(socketserver.StreamRequestHandler):
timeout = 5 * 60
def server_bind(self):
self.socket.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEADDR, 1)
self.socket.bind(self.server_address)
def handle(self):
challenge(self.rfile, self.wfile)
if __name__ == "__main__":
import sys
if len(sys.argv) == 1:
print("run with either stdin or socket")
exit(1)
if sys.argv[1] == "stdin":
challenge(sys.stdin.buffer, sys.stdout.buffer)
elif sys.argv[1] == "socket":
with socketserver.ThreadingTCPServer(("0.0.0.0", 50007), MyTCPHandler) as server:
server.serve_forever()
This challenge requires me to retrieve the flag by utilizing my knowledge of AES encryption. So it looks like I’m giving a few plaintexts to input that return ciphertext. These are the only hints I have for a solution to figuring out what the flag is. So, after I input each plaintext from the list of plaintexts given, I receive output like:
Sandra R. Jackson;reg2;1728 Goldie Lane
ba08daca777da10f5f955c5eb3f2f8c9edca01da9b0538a785012bd6cd2c39b3536105e53cc05b3b5ce10c852ee00956f881d70f2a4b70
Leo N. Shatley;reg1;2251 Sunburst Drive
f377031278ad25b542ee459522b48d464386b3ec61bbfa28bceaa92ffed4d7f5a4d7e09ba2a8f62e1e674ffd8afa4df4c598934ec5700f
Faye S. Ramsey;reg2;3186 Froebre Street
ca9dcce766bdb70e05dbaef485d4d7a59e551d3bfab385028747144d65665a40d6c422b487217a3c2d0794265d15c24f0e90034c65f565
Charles C. Felix;reg3;2726 Locust Court
ad1b8ed4ce0993bacfb9a5de1f2b8d6e96570310a5244dd4dd3525c858f028562e8cc6e8dba0eb8e3559112e8da88e2f8e8ebda7891902
Looking at the code, it seems like after a plaintext has been received that meets the requirements specified in the if statement, the program randomly choose one of the plaintexts from the given list of plaintexts and encrypts it. However, in the beginning of the program, the flag is actually added to the given list of plaintexts, so one of the ciphertexts returned is most likely (since random selection is used) the flag encrypted using AES encryption. There are a variety of tools online that can decrypt AES encrypted texts, but I still need to figure out what the key is, of whatever byte size since “none” is given in the “secrets.token_bytes” method.
Hash Consulting
Challenge Description:
At Voter Security Inc., our hashes keep getting cracked. To find out why, we had a series of meetings shifting the blame around. Then we decided to put off accepting responsibility by hiring consultants instead. We’d like to pay you a large amount of money to write a proof of concept that recovers rulesets.
handout:
import hashlib
import string
import secrets
import socketserver
import struct
import subprocess
import tempfile
from hashlib import sha256
from generate_rules import generate_random_rule
NUM_WORDS = 100
NUM_RULES = 10
NUM_HASHES = 100
SUCCESS_RATE = 0.7
POW_HARDNESS = 9999999
# NUM_WORDS words randomly from /usr/share/dict/words
with open("dictionary.txt") as f:
DICT = f.read().strip().split("\n")
assert len(DICT) == NUM_WORDS
with open("dictionary2.txt") as f:
DICT = f.read().strip().split("\n")
assert len(DICT) == 1
assert DICT[0] == "IBOHjYMP4wIvjXw"
def test_pow(chall, solution, hardness):
h = sha256(chall + struct.pack("<Q", solution)).hexdigest()
return int(h, 16) < 2 ** 256 / hardness
def printable_bytes(length=10):
characters = string.ascii_letters + string.digits
return "".join(secrets.choice(characters) for _ in range(length)).encode()
def challenge(ioin, ioout):
challenge = printable_bytes()
ioout.write(challenge + b"\n")
if not test_pow(challenge, int(ioin.readline().strip()), POW_HARDNESS):
ioout.write(b"bye\n")
return
ioout.write(b"welcome\n")
rules = [
"".join([generate_random_rule() for y in range(secrets.randbelow(3) + 1)])
for x in range(NUM_RULES)
]
print(rules)
with tempfile.NamedTemporaryFile(mode="w+") as rule_file:
rule_file.write("\n".join(rules) + "\n")
rule_file.flush()
p = (
subprocess.run(
["hashcat", "-r", rule_file.name, "--stdout", "dictionary.txt"],
capture_output=True,
)
.stdout.strip()
.split(b"\n")
)
assert len(p) == NUM_WORDS * NUM_RULES
passwords = [secrets.choice(p[:-NUM_RULES]) for k in range(NUM_HASHES)]
hashes = [hashlib.md5(pw + b"ahNgah7d").hexdigest() for pw in passwords]
ioout.write("\n".join(hashes[:-1]).encode())
ioout.write(b"\nsend guesses\n")
recvd = set()
for x in range(NUM_RULES):
recvd.add(ioin.readline().strip())
print(recvd)
with tempfile.NamedTemporaryFile(mode="w+") as rule_file:
rule_file.write("\n".join(rules) + "\n")
rule_file.flush()
p = (
subprocess.run(
["hashcat", "-r", rule_file.name, "--stdout", "dictionary2.txt"],
capture_output=True,
)
.stdout.strip()
.split(b"\n")
)
assert len(p) == NUM_RULES
tofind = set(p)
print(tofind)
suc = len(tofind & recvd) / len(tofind)
ioout.write(f"you got {suc}: ".encode())
if suc >= SUCCESS_RATE:
print(suc)
with open("flag.txt", "rb") as f:
ioout.write(f.read() + b"\n")
else:
ioout.write(b"sorry\n")
class MyTCPHandler(socketserver.StreamRequestHandler):
timeout = 5 * 60
def server_bind(self):
self.socket.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEADDR, 1)
self.socket.bind(self.server_address)
def handle(self):
challenge(self.rfile, self.wfile)
if __name__ == "__main__":
import sys
if len(sys.argv) == 1:
print("run with either stdin or socket")
exit(1)
if sys.argv[1] == "stdin":
challenge(sys.stdin.buffer, sys.stdout.buffer)
elif sys.argv[1] == "socket":
with socketserver.ThreadingTCPServer(
("0.0.0.0", 50007), MyTCPHandler
) as server:
server.serve_forever()
